A differential equation is relation between a collection of functions and their derivatives. An ordinary differential equation is a differential equation that relates functions of one variable to their derivatives with respect to that variable. A partial differential equation is a differential equation that relates functions of more than one variable to their partial derivatives. Differential equations arise naturally in the physical sciences, in mathematical modelling, and within mathematics itself. For example, Newton Seconds Law , which describes the relationship between acceleration and position, can be stated as the ordinary differential equation
The heat equation in one space variable, which describes how heat diffuses through a straight rod, is the partial differential equation

Here u(x, t) is the temperature of the rod at position x and time t and α is a constant that depends on how fast heat diffuses through the rod.
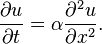
Taken From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differential_calculus
0 comments:
Post a Comment